Eng
Stepping in place on the rotating platform (circular treadmill) while holding on to a support activates the intra- and extra-rotatory muscles of the lower limbs. They rotate the limbs on the pelvis during the lifting phase of the limb and the pelvis and trunk on the leg during the supporting phase of the stepping.
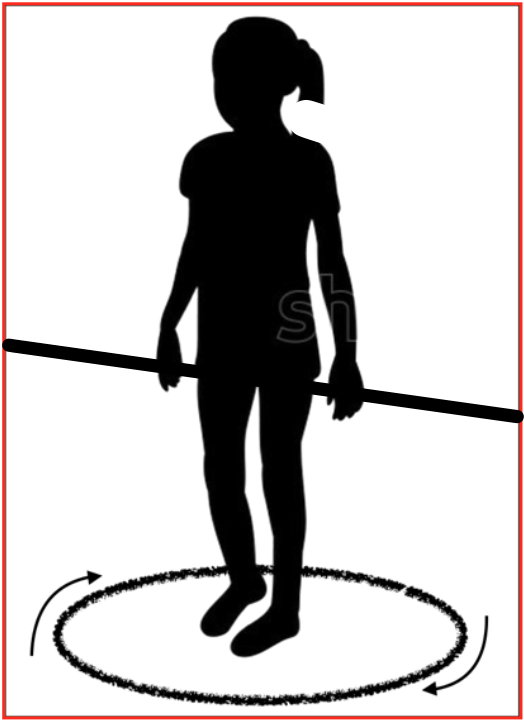

What is to be avoided?
Hesitations and stumbles while walking, with particular reference to walking on non-straight paths.
Falls, with particular attention to walking with changes of direction.
Falls due to internal disturbances (e.g. fatigue) or external disturbances (slipping or bumping into something).
Who are the main beneficiaries of the proposed treatment?
Fragile persons (presence of concomitant or pre-existing pathologies listed in the website of the NHS).

The following frailty criteria are reported in Fried et al. (2001): unintentional weight loss of more than 5 kg in one year; general feeling of fatigue (reported by the patient); muscular deficit (reduced muscle strength); reduced walking speed; physical inactivity.
People with multiple sclerosis, for whom the incidence of falls is estimated at over 50%, similar to that observed in adults over 80.
People living in therapeutic communities, suffering from health problems that limit their autonomous functional abilities, and who often need help with their daily activities.
People with anxiety who are afraid of falling.
People suffering from balance disorders of various origins or undergoing anticoagulant treatment.
In which specific conditions is the treatment particularly indicated?

Parkinson’s disease.
Stroke with impaired function of the lower limbs.
Cerebral palsy.
Walking with steppage.
Ataxia.
Incomplete spinal cord injury.
Sarcopenia, Ostheoporosis.
What can be rehabilitated?
Walking after femoral osteosynthesis surgery.
Walking after hip arthroplasty.
Walking after scoliosis surgery.
Walking and balance after prolonged bed rest.
Training and fitness
Many, if not all, of the movements involved in sporting activities involve the muscles that stabilise the trunk over the lower limbs and those that rotate the trunk in relation to the pelvis and lower limbs. The dynamic activation of these muscles using the rotating platform when walking in place is the best way of stimulating neuromuscular plasticity (Paillard, 2017) in this crucial part of the body.
Repeated Sprint Ability in football.
Skiing, golf, hammer and shot put, discus throwing, dance.
Any other activity involving the activation and control of internal and external rotation of the legs on the pelvis and the pelvis on the trunk.
Any other activity requiring control of the centre of body mass.

References
O’Malley N, Clifford AM, Conneely M, Casey B, Coote S. Effectiveness of interventions to prevent falls for people with multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease and stroke: an umbrella review. BMC Neurol. 2021 Sep 29;21(1):378.
Paillard T. Plasticity of the postural function to sport and/or motor experience. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017 Jan;72:129-152.
Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman AB, Hirsch C, Gottdiener J, Seeman T, Tracy R, Kop WJ, Burke G, McBurnie MA; Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research Group. Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001 Mar;56(3):M146-56.
Back to website 👆

To everything turn, turn, turn
There is a season turn, turn, turn
And a time to every purpose under Heaven
A time to be born, a time to die
A time to plant, a time to reap
A time to kill, a time to heal
A time to laugh, a time to weep
[from ‘Turn! Turn! Turn!’ (1959), music by Pete Seeger (1919-2014)]